On 1 November, Radiflow’s Chief Information Security Officer and VP of Business Development, Rani Kehat, published an informative article in LinkedIn on the latest version of The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) 4.0. In this blog, we want to provide some background on CVSS for those in the OT security (and IoT OT security as well) community who might not be familiar with it. CVSS is a very large and detailed subject – too big for a blog – but we can convey the basics and encourage you to read the specification for all the gory details.
About CVSS
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System is an open framework for communicating the characteristics and severity of software vulnerabilities. It is not a measure of risk, but is useful to state-of-the-art Risk Management solutions as will be described later in this blog.
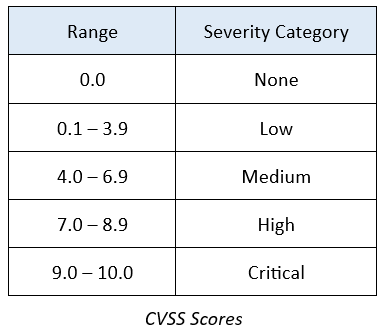
CVSS is well suited as a standard measurement system for industries and organizations that require accurate and consistent vulnerability severity scores. The CVSS score is represented simply as a number from 0 – 10 that represents the severity of a security vulnerability. The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) provides CVSS assessments for all published CVE records.
Some Use Cases
Industrial organizations can use CVSS to calculate the severity of vulnerabilities discovered on their systems and as a factor for prioritizing vulnerability remediation activities.
Software developers can use CVSS scores to prioritize security tests to ensure that known and serious vulnerabilities are removed or mitigated during development.
Risk Management solution providers can incorporate CVSS in their risk assessments for accuracy and compliance with standards.
Some security standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, rely on CVSS to determine level of compliance. For example, PCI DSS looks rejects as non-compliant a CVSS score of 4.0 or higher.
Determining CVSS Scores
CVSS consists of four metric groups: Base, Threat, Environmental, and Supplemental.
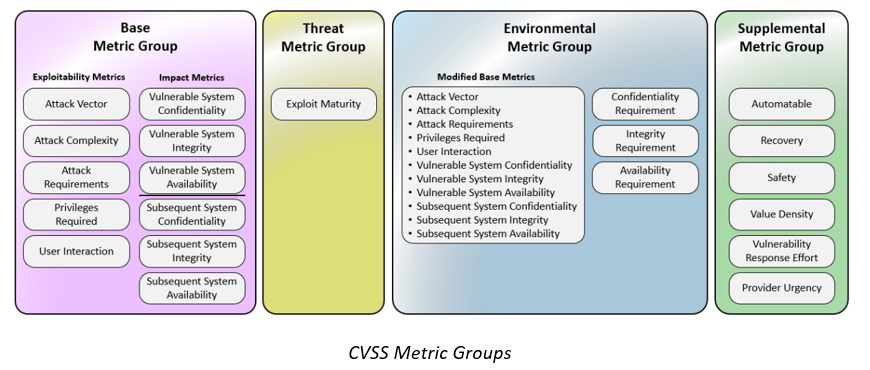
Base metric values are combined with default values that assume the highest severity for Threat and Environmental metrics to produce a score ranging from 0 to 10. To further refine a resulting score, Threat and Environmental metrics are modified according to applicable threat intelligence and/or environmental considerations.
CVSS and Risk Assessment
In his article, Rani describes what he especially likes about the new capabilities and features of CVSS 4.0, addressing those that are especially beneficial for ICS risk assessment.
Radiflow’s Risk Assessment and Management platform, CIARA, makes great use of the new capabilities of CVSS 4.0. CIARA is a data-driven platform that records network activity including asset functions, communications (regardless of protocol), and more. Connected to vulnerability and threat intelligence databases, CIARA automatically simulates multi-instances of initial access and network operations to identify possible attack vectors and their effects upon known, exploitable asset vulnerabilities.
The outcomes of CIARA’s simulations are:
Serving as a decision-support tool, CIARA empowers stakeholders to optimize their OT- security expenditure and ensure the effectiveness of threat-mitigation controls. By following CIARA’s mitigation roadmap, organizations are able to divert security expenditure from mitigations that marginally reduce risk (given the actual threats the network faces) to those that produce the greatest cybersecurity ROI.
Contact our team today for more information and to discover how you can ensure the best level of ICS security for your OT network.

CIARA by Radiflow uses CVSS 4.0 scores to help determine risk in OT networks and systems

One Weak Password, Full Process Control: Inside Norway’s 2025 Dam Cyberattack

Project Management in OT/ICS Projects with IEC 62443 and MITRE ATT&CK using Radiflow

Rogue Communication Modules in Solar Inverters: Radiflow Threat Analysis